Donate
An opportunity to support a revolution in life skills education.
Curriculum for Life plays a unique role in making Life Skills Learning available for every young person’s educational experience.
With youth at our centre, learning resources are co-created by and for young people and educators in their settings. Resources created are open access so that everyone can benefit.
Our network is centred around a small core team, co-funded collaborative partnerships and numerous contributors who volunteer their time and expertise.
Supporting CfL helps us to grow a network that responds to the issues that young people encounter and offers a high impact return for donors.
Your donations will contribute to our core funding, and the following examples showcase our work.
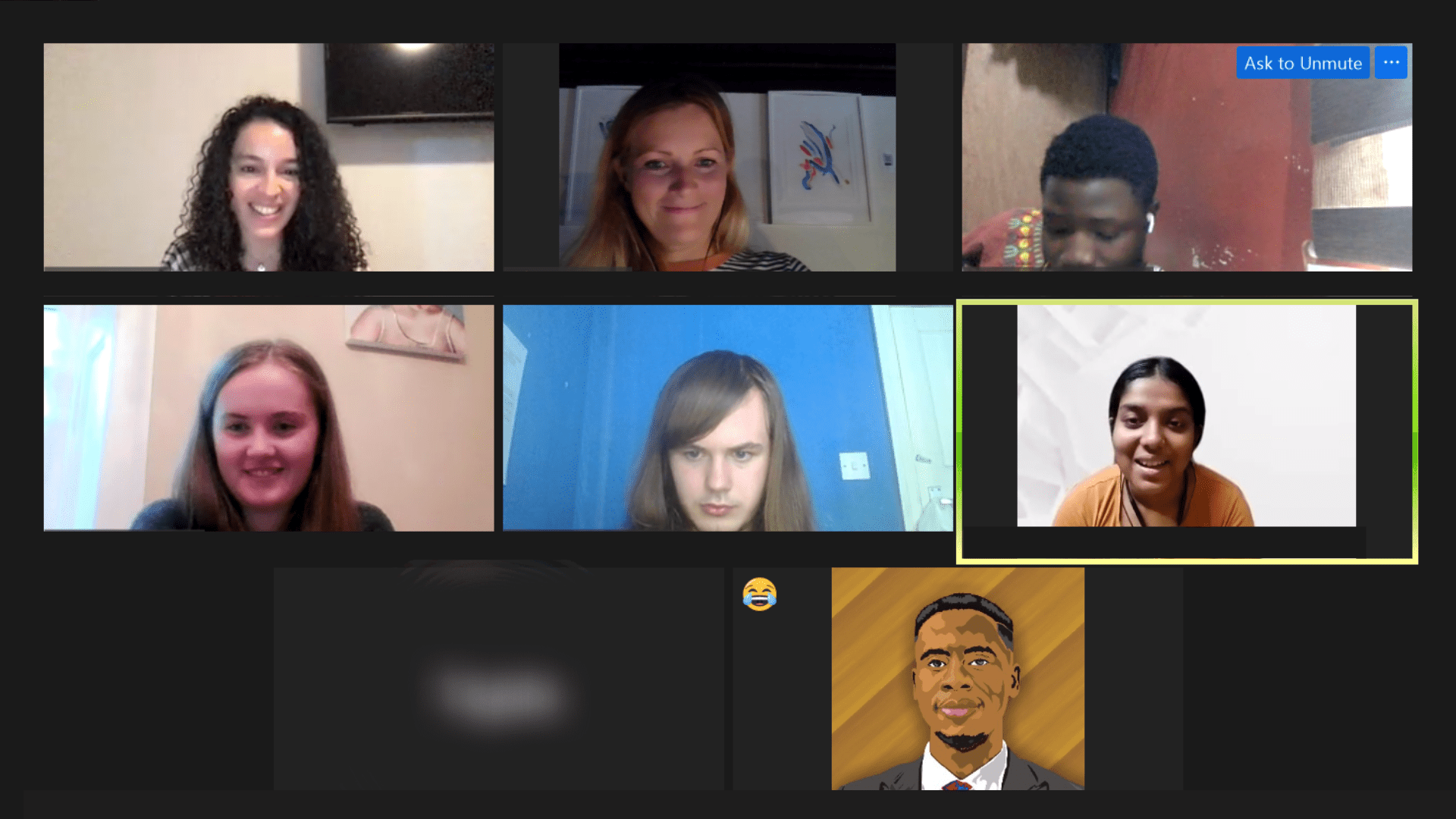
Your support enables young people from different socioeconomic groups to participate in our intergenerational co-creation sessions, ensuring that we run an inclusive co-creation system with a globally representative youth voice.
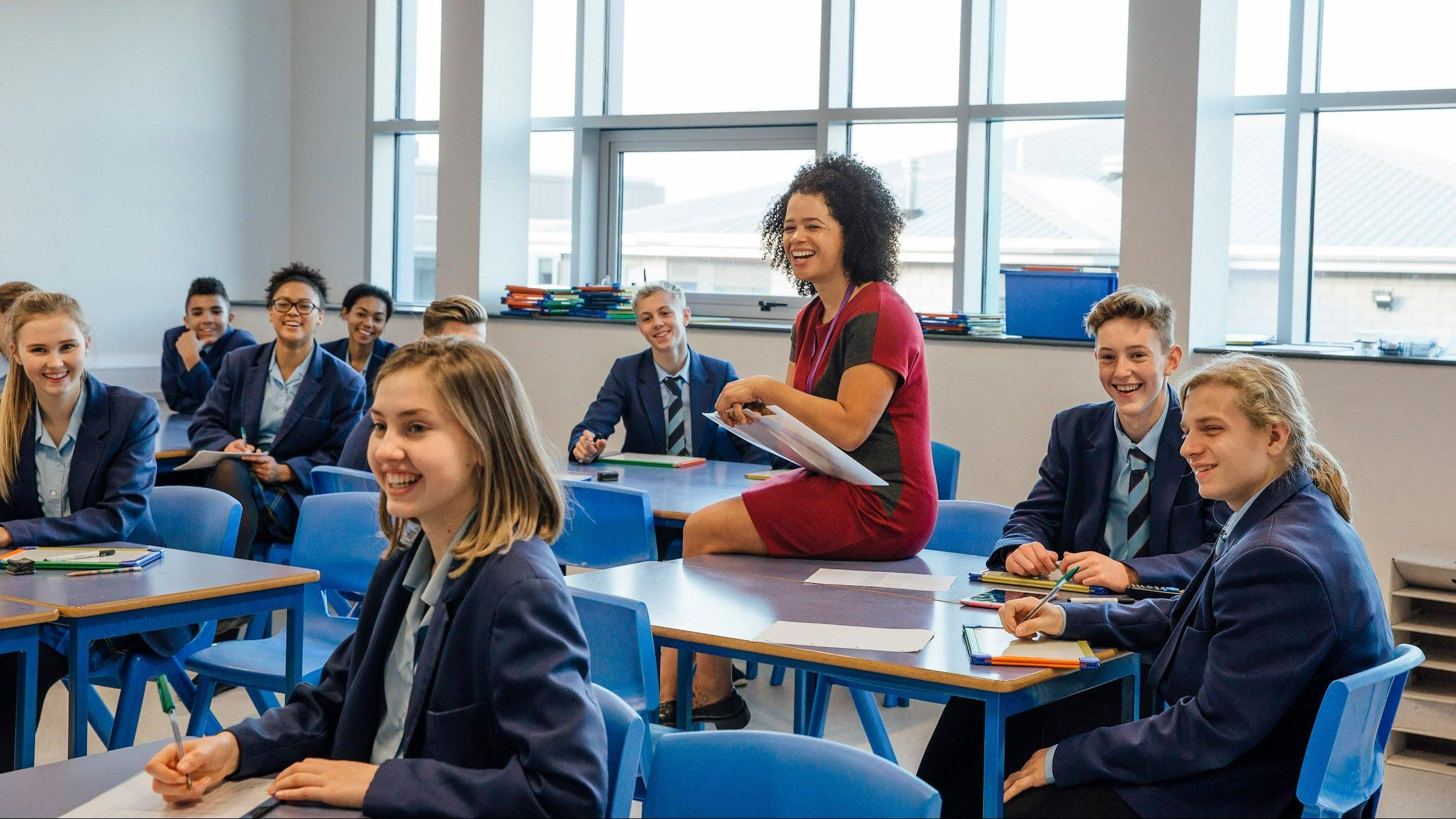

With your help we are able to give teachers the tools and assistance they need to test out our resources and methods in their classrooms and other settings, allowing young learners to gain valuable life skills.

Your contribution supports the development and extension of our learning platform, which will make all CFL lessons, facilitation manuals, and user-friendly resources available to learners and educators worldwide at no cost.
Help us help others!
Do you want to empower a brighter future by supporting every young person to flourish?
Your Support:
- Enriches learners with vital life skills
- Equips teachers with essential tools
- Expands free access to crucial educational resources

A gift donation from you will help us co-create impactful Life Skills Learning resources, freely available for all:
Life Skills for Wellbeing (14-15 yrs)
Learning focus: Support learners to discover and notice the essentials of wellbeing, such as connection, learning, being active and giving.


Self-Awareness
Self-Awareness is the ability to see ourselves clearly and objectively through reflection and introspection. It includes recognition of ourselves, our context, our personal qualities, our strengths and weaknesses, our values and beliefs, likes and dislikes, dreams and aspirations, etc., contributing towards our sense of identity. It is also the ability to recognise the contradiction between our aspirations, abilities and values. It is knowledge of our feelings and emotions and how they influence our decisions and behaviour.
Self-Awareness helps us recognise when we are stressed or under pressure. It allows us to see things from the perspective of others, practice self-control, work creatively and productively, and experience pride in ourselves and our work thus contributing to an overall sense of confidence and optimism.
Self-Awareness In Action
The person will be able to:
- Understand their emotions.
- Accurately label emotions and recognise how they are linked to behaviour.
- Analyze how thoughts affect decision making and responsible behaviour.
- Identify their personal strengths and weaknesses.
- Develop personal skills and interests they desire to have.
- Identify their values and beliefs.
- Analyse how personal qualities and values influence choices and successes.
- Accept themselves with a sense of optimism about personal abilities and skills.
- Recognise the different roles they play in the context of age, gender, family, community and school/working place.
- Recognise their rights and duties as individuals and their responsibility towards themselves and society.


Self-Management
Self-Management is the ability to regulate our emotions, thoughts and behaviours effectively in different situations. This includes managing stress, delaying gratification, keeping ourselves motivated and setting and working towards personal, academic and career goals. This skill also includes managing our time effectively in response to current or changing circumstances.
Self-Management helps in all domains of life and can be an important determinant of employment and life success and overall wellbeing.
Self-Management In Action
The person will be able to:
- Recognize how thoughts, emotions and behaviour are linked to personal well-being.
- Devise ways of managing personal well-being and achievement of goals.
- Find ways of expressing difficult emotions.
- Identify sources of support in their school, family and community that can offer timely help and guidance.
- Identify resources within themselves which can be accessed in adverse and upsetting situations. Identify sources of stress and then devise healthy and effective ways of responding to them.
- Consider time as an important factor whenever they plan activities and factor for unexpected situations or delays.
- Practise punctuality in their day-to-day lives and demonstrate other ways in which they can value their own as well as others’ time.
- Set realistic and achievable goals for themselves and measure progress on a regular basis.
- Show responsibility towards their physical health by being mindful of and making appropriate choices regarding their habits, routine and overall lifestyle.
- Resist the impulse to seize a short-term reward in preference to a more valuable long-term benefit.

Relationship Management
Relationship Management is the ability to form and maintain healthy, meaningful and rewarding relationships with diverse individuals and groups in both our personal as well as professional domains. It is an important leadership skill and includes the ability to have clear and assertive communication, be honest in our expression of views and emotions, have warm interactions with our family, friends, community, colleagues etc., offer honest and constructive feedback, resist various forms of social pressure and negotiate interpersonal conflicts in mutually beneficial ways. This skill includes both – being aware of our own emotions as well as being considerate of others’ emotions, as we navigate through various social interactions.
Relationship Management skills help us form deeper and richer connections with others in all areas of our life.
Relationship Management In Action
The person will be able to:
- Demonstrate good listening skills in daily interactions with friends, peers, teachers, family etc.
- Communicate clearly and assertively in their day-to-day interactions with others.
- Try out different ways to help out their friends and classmates.
- Seek and offer help when required.
- Express and share their emotions in an open and honest way with their friends, family, etc.
- Work cooperatively and effectively in groups.
- Form teams, influence team members, and boost team morale.
- Resist and manage peer pressure in an effective manner.
- Negotiate conflicts and navigate difficult social situations effectively.


Resilience
Resilience is the ability to persist, adapt or transform in the face of change in a way that upholds our basic identity. It is the process of adapting well in the face of hardships, trauma, failure, threats or significant stress, and achieving a sense of equilibrium. Resilience also refers to positive adaptation and the ability to regain mental health, after having experienced adversity.
Resilience is believed to improve learning and academic achievement. It contributes to reduced risk-taking behaviors including excessive drinking, smoking, and use of drugs. Resilient people are able to better manage difficult emotions and experience more positive emotions, which leads to good health outcomes.
Resilience In Action
The person will be able to:
- Adapt to change.
- Manage strong feelings and impulses.
- Make realistic plans and take steps to carry them out.
- Make a realistic appraisal of situations enabling acceptance of what cannot be changed.
- Have a positive view of themselves and have confidence in their strengths and abilities.
- Face unexpected challenges.
- Approach adversity as a solvable challenge.
Life Skills for Human-AI Collaboration (14-15 yrs)
Learning focus: Cultivating life skills for navigating and leveraging AI tools, now and in the future, emphasising empathy, ethical discernment, and collaborative spirit.


Creative Thinking
Creative Thinking is the ability to engage in the generation, evaluation and improvement of diverse ideas, which can result in original and effective solutions, advancement in knowledge and meaningful expressions of imagination. It involves making connections across topics, concepts, disciplines and methodologies.
Creative Thinking is a vital life skill which enables us to imagine, innovate and respond to unexpected or changing situations. It can improve other abilities like metacognition and problem-solving skills, as well as promote identity development, academic achievement, future career success and social engagement.
Creative Thinking In Action
The person will be able to :
- Follow new approaches and produce original ideas.
- See existing situations in new ways or improve on existing ideas.
- Act on intuition.
- Identify alternative explanations.
- Generate diverse and numerous ideas.
- Generate ideas that are relevant to the requirements of the problem/situation.
- Form unexpected combinations from available information to come up with solutions or new ideas.
- Engage in the task because they find it rewarding, enjoyable and challenging rather than for incentives offered.


Empathy
Empathy is the ability to emotionally understand what other people feel, see things from their point of view and context, imagine ourselves in their place and respond appropriately. Empathy is relating to others with acceptance, understanding, and sensitivity to their diverse backgrounds, experiences and perspectives, and taking action accordingly.
Empathy plays an important role in being a socially competent person with meaningful social relationships. The ability to empathise is important for promoting positive behaviours towards others, and facilitating social interactions and relationships, thus motivating altruistic behaviour. This skill also makes us challenge intolerance, bias and stereotyping when we see it.
Empathy In Action
The person will be able to:
- Listen well, pay attention to non-verbal communication and pick up subtle cues.
- Understand others’ perspectives and feelings.
- Show sensitivity towards others.
- Help other people based on their understanding of their needs and feelings.
- Respect and relate well to everyone, regardless of their diverse backgrounds.
- Alter the way they interact with others to fit with the others’ diverse needs and feelings.
- Appreciate others for their strengths and accomplishments.
- Provide constructive feedback to others to help them improve.
- Put the needs of others first and look for ways to improve their situations.


Adaptability
Adaptability is the ability to modify our thoughts and behaviour to effectively respond to uncertainty, new information, changed circumstances or different people. It includes adjustments in our thinking, emotions and behaviour in response to change, to demonstrate enhanced outcomes. It is our ability to respond to change and a willingness to learn new ways to accomplish work activities and objectives.
As a skill, Adaptability is essential to our psychological health, social success, and academic and workplace achievement.
Adaptability In Action
The person will be able to:
- Be open to accepting change.
- Learn new methods and practices as the situation requires.
- Look for ways to make changes work rather than only identifying why change will not work.
- Think and act effectively under pressure.
- Adjust timelines, results, and expectations appropriately when requirements change.
- Shift strategy or approach in response to the demands of a situation.

Decision Making
Decision Making is the ability to choose between two or more courses of action. It is the ability to identify and analyze the implications and consequences of our decisions. It is a process of making thoughtful, constructive and responsible choices about personal behaviour related to health, relationships, career and lifestyle, considering existing social, ethical and safety norms, in varied conditions.. It includes being able to make decisions independently and taking responsibility for our actions.
This key skill when imbibed at a young age contributes to a feeling of autonomy and also a sense of fulfilment. Decision Making is also proven to positively impact the attitude and effort we put into any task.
Decision Making In Action
The person will be able to :
- Make informed decisions based on their own experience and learning.
- Understand and evaluate the consequences of their decisions.
- Take personal responsibility for the consequences of their decisions.
- Consider others’ needs while making decisions.
- Evaluate the influence of social norms and authority on personal decision making.
- Apply ethical reasoning while making decisions.
- Make responsible decisions with respect to interpersonal and group relationships.
- Analyse how present decision making affects college and career choices.
- Evaluate the influence of personal biases and discrimination on personal decision making.
- Identify and evaluate strategies to resist pressure to engage in unsafe or unethical activities.
- Improve study habits and academic performance through responsible decision making skills.
Life Skills for Systems Thinking (8-16+ yrs)
Learning focus: Lessons that align life skills with the habits of systems thinking, collaboratively exploring these concepts through the prism of planetary stewardship.


Tolerance of Ambiguity
Tolerance of Ambiguity is the ability to perceive ambiguous situations as desirable, accept some uncertainty while making decisions, and a tendency to avoid thinking in a rigid manner. It is the degree to which we are comfortable with uncertainty, unpredictability, conflicting directions, and multiple demands. It manifests itself in our ability to operate effectively in an uncertain environment.
Tolerance of Ambiguity is seen as an important criterion for development of flexible, integrative, and independent thinking. Also, a significant and positive relationship has been found between creativity and tolerance of ambiguity.
Tolerance Of Ambiguity In Action
The person will be able to:
- Stay patient when being a part of an activity that they do not totally understand.
- Participate in a setting that is composed of people that do not share similar values.
- Enjoy working with people who have different values than themselves.
- Enjoy travelling and adjusting to new and unfamiliar situations.
- Manage their emotions in unpredictable and unfamiliar situations.


Perspective Taking
Perspective Taking is the ability to imagine and understand a situation based on how it appears to others and their cognitive and emotional response to it. It is the ability to recognize their points of view, experiences and beliefs even when different from our own. This recognition creates the basis of mutual understanding, leading to new learning, reshaping our social interactions and developing new world views that are broader and more inclusive in nature.
Overall, Perspective Taking promotes social bonds, unlocks the potential of diversity in teams, leads to creative solutions and diminishes the possibility and impact of stereotyping.
Perspective Taking In Action
The person will be able to:
- Practise active listening skills when their friends or group members are sharing their story or viewpoint.
- Identify the need to seek out and include views, opinions and experiences of their classmates, teammates and groups in general.
- Identify and acknowledge the experiences, feelings, and viewpoints of others even though they are different from their own.
- Find ways of expressing their emotions in ways that others can understand and accept, especially in times of conflicts and differences of opinion.

Information Synthesis
Information Synthesis is the ability to gather, analyze and evaluate information from various sources, make connections between the information found, and combine the recently acquired information with prior knowledge to create a new understanding. It includes the ability to check the authenticity and accuracy of the information, and an awareness of the short term and long term consequences of sharing of the information. This skill enables us to visualise and resolve contradictory findings.
Information Synthesis is a vital skill necessary to achieve personal, social, occupational and educational goals.
Information Synthesis In Action
The person is able to:
- Gather and use information effectively to accomplish a specific purpose.
- Determine the nature and extent of the information needed for a given task.
- Use multiple sources which address multiple perspectives, including opposing viewpoints.
- Evaluate the information and its sources critically before drawing a conclusion.
- Understand the economic, legal, and social issues surrounding the use of information.
- Access and use information ethically and legally.
- Build explicit connections between sources, including connections between contradictory sources, by identifying similarities, differences, relationships and patterns.


Ecological Literacy
Ecological Literacy refers to an understanding of our natural ecosystems and the ability to use this understanding for creating sustainable human societies without causing harm to the environment. It includes knowledge of the interconnectedness and interdependence of living and non-living systems around us and our symbiotic role as humans to preserve these systems.
Ecological Literacy is considered a necessary skill today when the conservation of earth’s natural resources has become an urgent priority for human society. This skill not only helps us to make environment-friendly choices in our daily lives but also purposefully reimagines and rebuilds our businesses and society at large in more sustainable ways.
Ecological Literacy In Action
The person will be able to:
- Show curiosity and compassion for Nature and its varied ecosystems, and ask questions related to the availability of natural resources, their use and abuse
- Recognise the fact that there can be no life without earth and its natural systems
- Demonstrate concern, commitment and action towards causes related to the environment.
- Take environment-friendly actions in their everyday lives like – waste segregation, not littering in public spaces, mindful usage of plastic products – including packaged food and water, mindful usage of water and electricity etc.
- Stay consistent with the environment-friendly choices they have made in their personal and professional lives.
- Evaluate the use of natural resources and the possible harm caused to the environment due to various human decisions, choices and actions.
- Innovate ideas and solutions that can help businesses, institutions and human communities at large to adopt sustainable modes of living.
Life Skills for Climate Justice (8-16+ yrs)
Learning focus: A CfL Youth Core Circle led initiative to co-create, implement and deploy learning experiences about taking care of ourselves and the planet.


Ecological Literacy
Ecological Literacy refers to an understanding of our natural ecosystems and the ability to use this understanding for creating sustainable human societies without causing harm to the environment. It includes knowledge of the interconnectedness and interdependence of living and non-living systems around us and our symbiotic role as humans to preserve these systems.
Ecological Literacy is considered a necessary skill today when the conservation of earth’s natural resources has become an urgent priority for human society. This skill not only helps us to make environment-friendly choices in our daily lives but also purposefully reimagines and rebuilds our businesses and society at large in more sustainable ways.
Ecological Literacy In Action
The person will be able to:
- Show curiosity and compassion for Nature and its varied ecosystems, and ask questions related to the availability of natural resources, their use and abuse
- Recognise the fact that there can be no life without earth and its natural systems
- Demonstrate concern, commitment and action towards causes related to the environment.
- Take environment-friendly actions in their everyday lives like – waste segregation, not littering in public spaces, mindful usage of plastic products – including packaged food and water, mindful usage of water and electricity etc.
- Stay consistent with the environment-friendly choices they have made in their personal and professional lives.
- Evaluate the use of natural resources and the possible harm caused to the environment due to various human decisions, choices and actions.
- Innovate ideas and solutions that can help businesses, institutions and human communities at large to adopt sustainable modes of living.


Leadership
Leadership is the ability to motivate and organise a group of people towards achieving a common goal. It is the ability to gain the trust and respect of group members by behaving responsibly and in a fair manner, and putting others’ needs before our own. It includes the ability to understand strengths and vulnerabilities of group members, so as to align them with tasks that optimize their performance. Leadership is also the ability to cause changes in other people and social systems.
Leadership skills benefit every aspect of our lives by helping in the development of key personal qualities such as perseverance, being committed and responsible, resilience, self-confidence, etc. Leaders use interpersonal and problem-solving skills to influence and guide others towards change.
Leadership In Action
The person will be able to:
- Lead a group towards achieving a goal.
- Delegate tasks to group members.
- Accept suggestions and inputs from the group members.
- Express confidence in others and their ability to contribute to the group.
- Make others feel valued in the group.
- Influence others through effective use of words and actions.
- View challenges as things that can be overcome with effort and innovative thinking.
- Be receptive to new and unfamiliar ideas, perspectives and experiences.
- Show resilience in tough situations.


Self-Esteem
Self-Esteem is our sense of our own value or worth, or the extent to which we value, approve of, appreciate or like ourselves. It can be a favourable or unfavourable attitude towards ourselves, and includes our evaluation of our thoughts and feelings overall in relation to ourselves. Expressing personal emotions, attitudes, and thoughts are highly associated with self-esteem.
Self-Esteem is seen as a critical factor in personal well-being as our self-esteem contributes to our psychological health, social adjustment, and quality of life.
Self-Esteem In Action
The person will be able to:
- Speak up and tell others their opinions in a respectful manner.
- Appreciate themselves and other people.
- Make their own decisions.
- Recognize and accept a wide range of feelings, both positive and negative.
- Handle criticism without taking it personally.
- Accept and learn from their mistakes when they fail.
- Accept challenges and take risks in order to grow.
- Aware of their values and live their lives accordingly.
- Respect others and accept them as they are without trying to change them.


Resourcefulness
Resourcefulness is the ability to adapt to new or different situations, think creatively, find solutions and make the best use of the available resources. This ability helps us consider all possible ways for attaining what we desire and also make good use of the opportunities available to us. It includes working collaboratively in teams or with group members and optimizing their skills and resources towards attainment of goals.
Research has shown that students who are resourceful tend to perform well even under stress and adversity. Resourcefulness can be considered as one of the important skills to being active, thoughtful and participating members and leaders in society.
Resourcefulness In Action
The person will be able to:
- Come up with multiple approaches to working towards a goal.
- Brainstorm alternative solutions to various problems.
- Show the readiness to experiment and try out new methods.
- Show curiosity and engage with their environment and the people around them.
- Build an active network of friends and acquaintances.
- Build resources for personal as well as social purposes.
- Demonstrate perseverance by trying out all possible means to attain their goals.
- Seek help, information and perspectives of individuals or groups who can contribute towards their goal or purpose.
- Demonstrate awareness of their own skills, talents and strengths.
Life Skills for Supporting Young Refugees (8-16+ yrs)
Learning focus: In partnership with Second Tree, we will co-create lessons that nurture life skills for positive interpersonal and environmental relationships and holistic growth for young refugees in Greece.


Decision Making
Decision Making is the ability to choose between two or more courses of action. It is the ability to identify and analyze the implications and consequences of our decisions. It is a process of making thoughtful, constructive and responsible choices about personal behaviour related to health, relationships, career and lifestyle, considering existing social, ethical and safety norms, in varied conditions.. It includes being able to make decisions independently and taking responsibility for our actions.
This key skill when imbibed at a young age contributes to a feeling of autonomy and also a sense of fulfilment. Decision Making is also proven to positively impact the attitude and effort we put into any task.
Decision Making In Action
The person will be able to :
- Make informed decisions based on their own experience and learning.
- Understand and evaluate the consequences of their decisions.
- Take personal responsibility for the consequences of their decisions.
- Consider others’ needs while making decisions.
- Evaluate the influence of social norms and authority on personal decision making.
- Apply ethical reasoning while making decisions.
- Make responsible decisions with respect to interpersonal and group relationships.
- Analyse how present decision making affects college and career choices.
- Evaluate the influence of personal biases and discrimination on personal decision making.
- Identify and evaluate strategies to resist pressure to engage in unsafe or unethical activities.
- Improve study habits and academic performance through responsible decision making skills.


Emotional Regulation
Emotional Regulation is the ability to be aware of, understand and accept our own emotions and control impulsive behaviours when experiencing difficult emotions. It includes the ability to modify strategies for managing our emotions according to situational demands and goals. Emotional regulation takes place through problem solving, assertive behaviour, reevaluation of the situation and de escalation of emotions.
Besides the obvious benefits such as feeling better in the immediate term, strong emotional regulation skills can also enhance long-term wellbeing, improve performance at work, enrich personal relationships and lead to better overall health.
Emotional Regulation In Action
The person will be able to:
- Identify, understand and accept their emotions.
- Express their emotions clearly and openly to others in ways appropriate to the situation.
- Express their feelings and opinions without hurting or disrespecting others.
- Reflect on possible consequences before expressing an emotion or viewpoint.
- Control impulsive behaviour.
- Express hurt without withdrawal, blame or aggression.
- Respond to upsetting situations in healthy and responsible ways.
- Use strategies that allow them to reduce the intensity of their emotions when they need to.


Relationship Management
Relationship Management is the ability to form and maintain healthy, meaningful and rewarding relationships with diverse individuals and groups in both our personal as well as professional domains. It is an important leadership skill and includes the ability to have clear and assertive communication, be honest in our expression of views and emotions, have warm interactions with our family, friends, community, colleagues etc., offer honest and constructive feedback, resist various forms of social pressure and negotiate interpersonal conflicts in mutually beneficial ways. This skill includes both – being aware of our own emotions as well as being considerate of others’ emotions, as we navigate through various social interactions.
Relationship Management skills help us form deeper and richer connections with others in all areas of our life.
Relationship Management In Action
The person will be able to:
- Demonstrate good listening skills in daily interactions with friends, peers, teachers, family etc.
- Communicate clearly and assertively in their day-to-day interactions with others.
- Try out different ways to help out their friends and classmates.
- Seek and offer help when required.
- Express and share their emotions in an open and honest way with their friends, family, etc.
- Work cooperatively and effectively in groups.
- Form teams, influence team members, and boost team morale.
- Resist and manage peer pressure in an effective manner.
- Negotiate conflicts and navigate difficult social situations effectively.

Communication
Communication is the ability to express ourselves and respond to people, both verbally and non-verbally, in ways that are appropriate to our culture and situation. This includes listening attentively and respectfully; expressing our opinions and desires, needs and fears in an assertive manner; as well as being able to ask for advice and help in times of need. It is a way of connecting with others by conveying our ideas, facts, thoughts, feelings, and values.
Effective Communication helps us better understand a person or situation and enables us to resolve differences, build trust and respect, and create environments where creative ideas, problem solving, affection, and caring can flourish.
Communication In Action
The person is able to:
- Listen actively without interrupting their peers, friends, teachers, family, etc.
- Recognise when to listen or speak.
- Express their thoughts clearly using verbal and para verbal cues.
- Express themselves in a variety of ways.
- Say ‘’no’’ in an assertive manner without being disrespectful.
- Consider others’ opinions and feelings before responding.
Life Skills for Global Citizenship (8-16+ yrs)
Learning focus: Lessons will hone young people’s citizenship skills, empowering them to navigate local challenges with a global perspective.


Negotiation
Negotiation is the ability to solve interpersonal problems and conflicts, by being assertive and cooperative, using logic and persuasion. It is the ability to be respectful and to disagree without threatening the wellbeing of others. It involves defining the problem, identifying a strategy and to proceed, keeping in mind the complexity of the emotions involved and the consequences for both parties. It requires persistence while interacting with the people involved and engaging with the process until a conclusion is reached.
Negotiation skills can help change attitudes, prevent or manage disagreements and misunderstandings, and improve relationships. They enhance our abilities to protect ourselves from exploitation, abuse and bullying.
Negotiation In Action
The person will be able to:
- Listen to others’ points of view attentively.
- Be respectful of others’ views and concerns, even while disagreeing.
- Prevent or manage disagreements and misunderstandings.
- Use verbal arguments over violence.
- Apply logic while presenting their arguments.
- Identify the root problem in a conflict situation.
- Change others’ attitudes to align with their own ideas.


Conflict Resolution
Conflict Resolution is the ability to resolve a dispute or a conflict, when there is disagreement, contradiction or incompatibility among two or more individuals or groups, by meeting at least some of each side’s needs and addressing their interests. It includes the ability to communicate and negotiate in a manner that can help the parties arrive at an agreement without hurting the relationship they share as well as the goals they feel committed to.
Conflict Resolution is considered an important life skill at an interpersonal as well as global level. Resolving conflicts can lead to constructive problem-solving and peaceful collaboration among individuals and groups.
Conflict Resolution In Action
The person will be able to:
- Show willingness to examine reasons for a conflict.
- Demonstrate a willingness to engage in constructive dialogue.
- Practise self-regulation skills by taking charge of their own emotions and being aware of those of others, thereby behaving accordingly.
- Seek and evaluate different perspectives towards resolving a situation.
- Practise assertiveness and cooperation in a balanced way.
- Show willingness and flexibility to compromise.

Compassion
Compassion is our ability to feel for others when they are in pain and be motivated to take action to relieve their suffering. It includes five essential elements – recognizing other people’s pain, accepting that human suffering is universal, feeling for the sufferer, tolerating the discomfort it causes to us without being judgmental and feeling motivated to help. It includes the aspect of Global Compassion which refers to compassion felt toward others regardless of their relationship with us, their status, background, membership to any group, and overall circumstances.
Compassion is an enduring skill that is associated with a range of positive attitudes and behaviours towards self, others and humanity as a whole. It is kindness and empathy extended beyond our own people thereby contributing to prosocial behaviour, conflict resolution, and peacekeeping at a global level.
Compassion In Action
The person will be able to:
- Recognize others’ feelings and emotions in particular situations.
- Identify their own feelings and emotions as they witness or hear about another person’s pain, suffering, hardships and misfortunes.
- Recognize how they feel when they hear about a person’s or a group’s suffering who is not related to them.
- Engage in simple acts of kindness on a day to day basis with people within their circle, as well as with strangers and animals.
- Come up with ways in which they can reach out and help others.
- Identify and validate people’s experiences across gender. race, ethnicity, geographical locations, religion, socio-economic strata etc. and show their readiness to help.
- Demonstrate a humane approach towards global problems.
- Commit to causes and put together resources in order to mobilize help.


Perspective Taking
Perspective Taking is the ability to imagine and understand a situation based on how it appears to others and their cognitive and emotional response to it. It is the ability to recognize their points of view, experiences and beliefs even when different from our own. This recognition creates the basis of mutual understanding, leading to new learning, reshaping our social interactions and developing new world views that are broader and more inclusive in nature.
Overall, Perspective Taking promotes social bonds, unlocks the potential of diversity in teams, leads to creative solutions and diminishes the possibility and impact of stereotyping.
Perspective Taking In Action
The person will be able to:
- Practise active listening skills when their friends or group members are sharing their story or viewpoint.
- Identify the need to seek out and include views, opinions and experiences of their classmates, teammates and groups in general.
- Identify and acknowledge the experiences, feelings, and viewpoints of others even though they are different from their own.
- Find ways of expressing their emotions in ways that others can understand and accept, especially in times of conflicts and differences of opinion.
Life Skills for Inspiring Leadership (8-16+ yrs)
Learning focus: Lessons will support young people to find out what it takes to be a leader and to experience how it feels to lead others to go beyond their own expectations.


Leadership
Leadership is the ability to motivate and organise a group of people towards achieving a common goal. It is the ability to gain the trust and respect of group members by behaving responsibly and in a fair manner, and putting others’ needs before our own. It includes the ability to understand strengths and vulnerabilities of group members, so as to align them with tasks that optimize their performance. Leadership is also the ability to cause changes in other people and social systems.
Leadership skills benefit every aspect of our lives by helping in the development of key personal qualities such as perseverance, being committed and responsible, resilience, self-confidence, etc. Leaders use interpersonal and problem-solving skills to influence and guide others towards change.
Leadership In Action
The person will be able to:
- Lead a group towards achieving a goal.
- Delegate tasks to group members.
- Accept suggestions and inputs from the group members.
- Express confidence in others and their ability to contribute to the group.
- Make others feel valued in the group.
- Influence others through effective use of words and actions.
- View challenges as things that can be overcome with effort and innovative thinking.
- Be receptive to new and unfamiliar ideas, perspectives and experiences.
- Show resilience in tough situations.


Communication
Communication is the ability to express ourselves and respond to people, both verbally and non-verbally, in ways that are appropriate to our culture and situation. This includes listening attentively and respectfully; expressing our opinions and desires, needs and fears in an assertive manner; as well as being able to ask for advice and help in times of need. It is a way of connecting with others by conveying our ideas, facts, thoughts, feelings, and values.
Effective Communication helps us better understand a person or situation and enables us to resolve differences, build trust and respect, and create environments where creative ideas, problem solving, affection, and caring can flourish.
Communication In Action
The person is able to:
- Listen actively without interrupting their peers, friends, teachers, family, etc.
- Recognise when to listen or speak.
- Express their thoughts clearly using verbal and para verbal cues.
- Express themselves in a variety of ways.
- Say ‘’no’’ in an assertive manner without being disrespectful.
- Consider others’ opinions and feelings before responding.


Responsibility
Responsibility is the ability to recognize our role, purpose and appropriate response in a personal or social context and to proactively carry it out to the best of our ability. It involves both concrete action and concern for the needs of ourselves and others. It includes being motivated to take civic action for the greater good. It includes our ability to align our thoughts and behaviours with ethical actions to take care of ourselves and others around us.
There are two facets to Responsibility – personal and social. Personal Responsibility helps us become autonomous, grow in independence and confidence. Social Responsibility skills lead to prosocial behaviors, communicating concern for others and practising civic skills.
Responsibility In Action
The person will be able to:
- Make decisions considering basic personal physical safety.
- Participate in household chores proportional to their ability.
- Honour commitments, and be punctual and reliable.
- Maintain peace and follow norms in public spaces.
- Accept errors and consequences.
- Reflect on and communicate their needs.
- Engage in healthy self-evaluation.
- Judge risks and take them safely.
- Recognize rationale behind rules set down by family and school systems and follow them when they are not oppressive.
- Start forming an understanding of issues in the world, like the environment, human rights, social justice etc.


Creative Thinking
Creative Thinking is the ability to engage in the generation, evaluation and improvement of diverse ideas, which can result in original and effective solutions, advancement in knowledge and meaningful expressions of imagination. It involves making connections across topics, concepts, disciplines and methodologies.
Creative Thinking is a vital life skill which enables us to imagine, innovate and respond to unexpected or changing situations. It can improve other abilities like metacognition and problem-solving skills, as well as promote identity development, academic achievement, future career success and social engagement.
Creative Thinking In Action
The person will be able to :
- Follow new approaches and produce original ideas.
- See existing situations in new ways or improve on existing ideas.
- Act on intuition.
- Identify alternative explanations.
- Generate diverse and numerous ideas.
- Generate ideas that are relevant to the requirements of the problem/situation.
- Form unexpected combinations from available information to come up with solutions or new ideas.
- Engage in the task because they find it rewarding, enjoyable and challenging rather than for incentives offered.
Life Skills for Learning to Collaborate (8-16+ yrs)
Learning focus: Lessons will be centered on co-creation, project planning, and cultivating efficient collaborative strategies.

Collaboration
Collaboration is the ability to work interdependently and cooperatively in teams. It is an organised and coordinated activity between two or more people to realise shared goals and outcomes. It includes the ability to manage team dynamics and challenges, and learning from and contributing to the learning of others.
Collaboration is a key skill that enables individuals to get along and work effectively with others, including people from diverse cultures.
Collaboration In Action
The person will be able to:
- Work with others and co-create ideas.
- Communicate effectively with groups.
- Offer and accept help.
- Lead, delegate and follow while working in a group.
- Understand team members’ feelings and points of view.
- Agree and disagree with others effectively.
- Listen to others and debate respectfully.
- Be helpful and supportive of their peers.
- Accept and appreciate team members’ skills and abilities.
- Prioritize group interests to achieve a common goal.
- Accept and respect differences while working with diverse individuals.


Empathy
Empathy is the ability to emotionally understand what other people feel, see things from their point of view and context, imagine ourselves in their place and respond appropriately. Empathy is relating to others with acceptance, understanding, and sensitivity to their diverse backgrounds, experiences and perspectives, and taking action accordingly.
Empathy plays an important role in being a socially competent person with meaningful social relationships. The ability to empathise is important for promoting positive behaviours towards others, and facilitating social interactions and relationships, thus motivating altruistic behaviour. This skill also makes us challenge intolerance, bias and stereotyping when we see it.
Empathy In Action
The person will be able to:
- Listen well, pay attention to non-verbal communication and pick up subtle cues.
- Understand others’ perspectives and feelings.
- Show sensitivity towards others.
- Help other people based on their understanding of their needs and feelings.
- Respect and relate well to everyone, regardless of their diverse backgrounds.
- Alter the way they interact with others to fit with the others’ diverse needs and feelings.
- Appreciate others for their strengths and accomplishments.
- Provide constructive feedback to others to help them improve.
- Put the needs of others first and look for ways to improve their situations.


Open-Mindedness
Open-Mindedness is the ability and willingness to form and revise our views, impartially and objectively in the light of available evidence and argument. It is our ability to remain non-judgmental and have a liberal outlook that regards all ideas as equally worthy. It prevents us from making hasty judgements and fosters intellectual curiosity and an appreciation of diversity.
Open-Mindedness helps us seek feedback from external sources and be willing to look within and self-analyze, and also seek out assistance for perceived flaws.
Open-Mindedness In Action
The person will be able to:
- Adapt willingly and easily to change, both positive and negative.
- Accept feedback on self from others.
- Accept others’ perspectives.
- Accept and appreciate differences in others.
- Appreciate new aesthetic, cultural or intellectual experiences.
- Accept both past and present circumstances or feelings in life.
- Experiment with new technology.
- Experiment with unfamiliar and uncertain situations.
- Explore new and unfamiliar ideas and experiences, without personal opinion or judgement.


Participation
Participation is the ability to contribute actively to processes and situations, influencing tasks done and decisions taken. The ability to participate effectively is important for personal empowerment and agency, as well as the development of self-efficacy and social connectedness. Participation also leads to higher self-esteem and creativity.
In an educational setting, Participation encourages active learning, promotes equity amongst learners, fosters a sense of ownership of the school and empowers communities. Within a family, participation leads to stronger relationships and autonomy. In a socio-political setting, it allows children to make their concerns heard about the world they will inherit.
Participation In Action
The person will be able to:
- Engage with learning.
- Share their views and opinions.
- Collaborate towards a common goal.
- Get along well with their classmates and teachers.
- Contribute to a better school environment with discipline and shared responsibility.
- Contribute to family decisions, make their voice heard in the family.
- Avail opportunities for recreation, career, long term relationships, socializing.
- Exercise their rights as citizens.
Life Skills for Dynamic Teamwork (8-16+ yrs)
Learning focus: Lessons will strengthen teamwork for problem-solving and promote unity towards shared goals.

Problem Solving
Problem Solving is the ability to seek, identify and define the problem, generate alternatives or potential solutions, evaluate and choose between these and act on the chosen solution to reach a goal. It includes the process of using reasoning and analysis to look beyond the surface of a problem and understand the underlying causes to come to conclusions. It is also the process by which we identify or discover effective, adaptive or creative ways of handling problematic situations encountered in everyday living.
Problem Solving increases our involvement in the learning process. This creates opportunities for higher order thinking which increases our adaptability to our environment and helps us navigate through future trends and uncertainty.
Problem Solving In Action
The person will be able to:
- Recognise a problem situation.
- Identify the root cause of a problem situation or a conflict.
- Identify and sift out information relevant to a problem.
- Pay attention to relevant cues.
- Make interpretations based on patterns that emerge.
- Set goals and a plan of action.
- Evaluate progress towards an identified goal.
- Suggest various options to resolve an issue.
- Consider different sides to a problem, both the pros and cons.


Decision Making
Decision Making is the ability to choose between two or more courses of action. It is the ability to identify and analyze the implications and consequences of our decisions. It is a process of making thoughtful, constructive and responsible choices about personal behaviour related to health, relationships, career and lifestyle, considering existing social, ethical and safety norms, in varied conditions.. It includes being able to make decisions independently and taking responsibility for our actions.
This key skill when imbibed at a young age contributes to a feeling of autonomy and also a sense of fulfilment. Decision Making is also proven to positively impact the attitude and effort we put into any task.
Decision Making In Action
The person will be able to :
- Make informed decisions based on their own experience and learning.
- Understand and evaluate the consequences of their decisions.
- Take personal responsibility for the consequences of their decisions.
- Consider others’ needs while making decisions.
- Evaluate the influence of social norms and authority on personal decision making.
- Apply ethical reasoning while making decisions.
- Make responsible decisions with respect to interpersonal and group relationships.
- Analyse how present decision making affects college and career choices.
- Evaluate the influence of personal biases and discrimination on personal decision making.
- Identify and evaluate strategies to resist pressure to engage in unsafe or unethical activities.
- Improve study habits and academic performance through responsible decision making skills.


Resourcefulness
Resourcefulness is the ability to adapt to new or different situations, think creatively, find solutions and make the best use of the available resources. This ability helps us consider all possible ways for attaining what we desire and also make good use of the opportunities available to us. It includes working collaboratively in teams or with group members and optimizing their skills and resources towards attainment of goals.
Research has shown that students who are resourceful tend to perform well even under stress and adversity. Resourcefulness can be considered as one of the important skills to being active, thoughtful and participating members and leaders in society.
Resourcefulness In Action
The person will be able to:
- Come up with multiple approaches to working towards a goal.
- Brainstorm alternative solutions to various problems.
- Show the readiness to experiment and try out new methods.
- Show curiosity and engage with their environment and the people around them.
- Build an active network of friends and acquaintances.
- Build resources for personal as well as social purposes.
- Demonstrate perseverance by trying out all possible means to attain their goals.
- Seek help, information and perspectives of individuals or groups who can contribute towards their goal or purpose.
- Demonstrate awareness of their own skills, talents and strengths.


Initiative
Initiative is the ability that motivates us to independently engage with ideas, people and experiences with enthusiasm. It is our ability to contribute to preferred activities, seek new experiences, ask questions, and take on challenges. It includes the capacity to take action, be resourceful and introduce a new course of action when required, sustain motivation, and work towards an identified goal. Initiative hinges on the belief that outcomes depend on our own actions rather than fate, chance or others.
Initiative skills are linked to enterprise, taking charge, follow-through, determination, and leadership. These skills help us engage effectively with the world around us and motivate us to pursue our desired goals. People with skills of initiative tend to accept responsibility for their attitudes and behaviour, and gain the trust of others.
Initiative In Action
The person will be able to:
- Actively take part in their own learning.
- Show enthusiasm for learning by asking questions.
- Actively engage in ideas, projects and tasks.
- Take on increasingly complex roles and tasks independently.
- Work independently, define, prioritize and complete tasks without constant monitoring.
- Go beyond basic acquisition of skills to explore and expand their own learning and gain expertise.
- Identify and seek support in tasks that might be difficult to achieve by themselves.
Life Skills for Exploring Local Context (8-16+ yrs)
Learning focus: Lessons will enable students to delve into the tapestry of local landscapes by understanding social, cultural, and environmental dimensions, fostering a sense of connection and appreciation.


Learning to Learn
Learning to Learn is the ability to pursue and persist in learning, to organise our own learning, through effective management of time and information. It includes awareness of the learning process, our needs and preferred learning strategies, the strengths and weaknesses of our skills and qualifications; identifying available opportunities; and the ability to overcome obstacles in order to learn successfully. It means gaining, processing and assimilating new knowledge and skills as well as seeking and making use of available guidance and support.
Learning to Learn helps us build on prior learning and life experiences in order to use and apply knowledge and skills in a variety of contexts – at home, at work, in education and training. This is an imperative skill to survive and adapt to a constantly changing world.
Learning To Learn In Action
Learning to Learn in Action
The person will be able to:
- Think about how they learn best.
- Manage their time and work patterns.
- Persevere with learning.
- Concentrate for extended periods.
- Evaluate their own work.
- Learn to work collaboratively as part of the learning process.
- Dedicate time to learning autonomously.
- Reflect critically on the purposes and aims of learning.
- Seek advice, feedback and support when appropriate.
- Be open to constantly learning from their own experiences and from others.


Adaptability
Adaptability is the ability to modify our thoughts and behaviour to effectively respond to uncertainty, new information, changed circumstances or different people. It includes adjustments in our thinking, emotions and behaviour in response to change, to demonstrate enhanced outcomes. It is our ability to respond to change and a willingness to learn new ways to accomplish work activities and objectives.
As a skill, Adaptability is essential to our psychological health, social success, and academic and workplace achievement.
Adaptability In Action
The person will be able to:
- Be open to accepting change.
- Learn new methods and practices as the situation requires.
- Look for ways to make changes work rather than only identifying why change will not work.
- Think and act effectively under pressure.
- Adjust timelines, results, and expectations appropriately when requirements change.
- Shift strategy or approach in response to the demands of a situation.


Metacognition
Metacognition is the ability to understand our own thinking, recognise what we know and what we do not know, and organise our thinking processes accordingly. It refers to a set of processes we use to monitor ongoing thoughts so as to effectively control our own behaviour. It also includes our ability to monitor, regulate and control our own activities concerning learning and take effective responsibility for our own learning.
Metacognition plays an important role in essentially all cognitive tasks, from everyday behaviours and problem solving to expert performance in the various disciplines.
Metacognition In Action
The person is able to:
- Reflect on their own thoughts and behaviour.
- Reflect and identify what they know and do not know about a subject.
- Think and plan on how to approach a learning task.
- Identify distractions while working on a task.
- Evaluate their progress toward the completion of a task.
- Use appropriate skills and strategies to solve a problem.
- Self-assess and self-correct in response to the self-assessment.
- Develop greater awareness of their actions and the effects of the same on others and the environment.
- Exhibit maturity in accepting their own limits to change.


Resilience
Resilience is the ability to persist, adapt or transform in the face of change in a way that upholds our basic identity. It is the process of adapting well in the face of hardships, trauma, failure, threats or significant stress, and achieving a sense of equilibrium. Resilience also refers to positive adaptation and the ability to regain mental health, after having experienced adversity.
Resilience is believed to improve learning and academic achievement. It contributes to reduced risk-taking behaviors including excessive drinking, smoking, and use of drugs. Resilient people are able to better manage difficult emotions and experience more positive emotions, which leads to good health outcomes.
Resilience In Action
The person will be able to:
- Adapt to change.
- Manage strong feelings and impulses.
- Make realistic plans and take steps to carry them out.
- Make a realistic appraisal of situations enabling acceptance of what cannot be changed.
- Have a positive view of themselves and have confidence in their strengths and abilities.
- Face unexpected challenges.
- Approach adversity as a solvable challenge.
Life Skills for Resilient Learning (8-16+ yrs)
Learning focus: Lessons will promote a growth mindset and metacognitive skills, equipping students with resilience, resourcefulness, and reflection strategies for effective approaches to learning and tackling life’s challenges.


Social Awareness
Social Awareness is the ability to form connections and work with people from diverse backgrounds in terms of religion, caste, gender, socio-economic strata, geographical location etc. It is the ability to understand, empathise and accept people and practices that are different from our own. It is also the ability to recognise and exercise our rights and duties as responsible citizens.
Social Awareness includes being sensitive to local and global environmental concerns, being aware of and involved in addressing social issues, respecting and protecting the rights of others, especially those of vulnerable populations (women, children, elderly, people with disabilities, economically and socially marginalised communities etc.), thus contributing to the collective wellbeing of society.
Social Awareness In Action
The person will be able to:
- Recognise ways in which they and their peers are similar and different.
- Express interest in getting to know their friends’ native language and cultural practices.
- Articulate how a diverse set of friends or members in a team enhances their perspective and life in general.
- Determine the commonalities amongst diverse people – their basic needs, emotions, expectations from others etc.
- Analyze their community’s or neighbourhood’s needs/problems and put together a plan to address those.
- Recognise the vulnerabilities of others and be willing to accept, protect and even help, if needed.
- Show awareness of specific social causes, take a stance and use concrete steps towards addressing them.
- Get involved in organizations and civic bodies that help and contribute towards various social and environmental causes.


Curiosity
Curiosity is the ability to apply a sense of wonder and desire to learn or know something, without expecting a tangible reward. It is also about recognising an information gap and having an intrinsically motivated desire to close it. It includes seeking out information to better understand a wide range of topics and/or obtaining a depth of understanding in one topic area that goes beyond what is required.
Curiosity as a skill can positively affect learning and memory; lead to greater levels of attention and skill development and enhance feelings of mastery.
Curiosity In Action
The person will be able to:
- Try new things and relish new experiences.
- Show an inclination towards knowing new things, searching for answers and making connections.
- Enjoy learning about topics that are unfamiliar to them, as well as about others’ perspectives on these topics.
- Show interest and enjoy being part of diverse groups.
- Ask questions to find out what interests other people.
- Ask questions and find out why people behave the way they do.
- Seek out opportunities where deep thinking is required.
- Seek solutions to difficult conceptual problems.
- Show trust in one’s own natural instincts, thereby taking risks.
- Look for challenges and consider them as opportunities to grow.

Mastery Orientation
Mastery Orientation refers to our approach towards achievement where the focus is on achieving mastery of a task with an emphasis on acquiring new skills, learning and improving against self-set standards. It arises from the belief that we have control over factors related to our learning, that hard work and effort pays off, and that we have or can acquire strategies that will help us learn. With this attitude we are more likely to enjoy and seek challenges, persist in the face of obstacles, and view our failures as due to inadequate effort or poor strategy rather than lack of ability.
Research says that Mastery Orientation is highly adaptive and carries many positive qualities, including perseverance, seeking out challenges and a desire to learn.
Mastery Orientation In Action
The person will be able to:
- Engage in activities that will increase their knowledge and learning.
- Find satisfaction in just learning without being influenced by external performance indicators such as grades.
- Learn from their errors.
- Seek help when necessary.
- Change learning strategies when they don’t work.
- Focus on improving their personal or professional competence
- Judge their performance based on standards of self-improvement and progress.
- Demonstrate a sense of purpose and persist towards goals despite challenges.
- Open to taking on challenging or unfamiliar learning tasks.
- Focus on achieving mastery even in the absence of external validation or reward
- View success in terms of continuous improvement and learning.


Ecological Literacy
Ecological Literacy refers to an understanding of our natural ecosystems and the ability to use this understanding for creating sustainable human societies without causing harm to the environment. It includes knowledge of the interconnectedness and interdependence of living and non-living systems around us and our symbiotic role as humans to preserve these systems.
Ecological Literacy is considered a necessary skill today when the conservation of earth’s natural resources has become an urgent priority for human society. This skill not only helps us to make environment-friendly choices in our daily lives but also purposefully reimagines and rebuilds our businesses and society at large in more sustainable ways.
Ecological Literacy In Action
The person will be able to:
- Show curiosity and compassion for Nature and its varied ecosystems, and ask questions related to the availability of natural resources, their use and abuse
- Recognise the fact that there can be no life without earth and its natural systems
- Demonstrate concern, commitment and action towards causes related to the environment.
- Take environment-friendly actions in their everyday lives like – waste segregation, not littering in public spaces, mindful usage of plastic products – including packaged food and water, mindful usage of water and electricity etc.
- Stay consistent with the environment-friendly choices they have made in their personal and professional lives.
- Evaluate the use of natural resources and the possible harm caused to the environment due to various human decisions, choices and actions.
- Innovate ideas and solutions that can help businesses, institutions and human communities at large to adopt sustainable modes of living.
Life Skills for Innovative Solutions (8-16+ yrs)
Learning focus: Lessons will foster curiosity and creativity to build solutions and tackle challenges with fresh design and thinking approaches.


Curiosity
Curiosity is the ability to apply a sense of wonder and desire to learn or know something, without expecting a tangible reward. It is also about recognising an information gap and having an intrinsically motivated desire to close it. It includes seeking out information to better understand a wide range of topics and/or obtaining a depth of understanding in one topic area that goes beyond what is required.
Curiosity as a skill can positively affect learning and memory; lead to greater levels of attention and skill development and enhance feelings of mastery.
Curiosity In Action
The person will be able to:
- Try new things and relish new experiences.
- Show an inclination towards knowing new things, searching for answers and making connections.
- Enjoy learning about topics that are unfamiliar to them, as well as about others’ perspectives on these topics.
- Show interest and enjoy being part of diverse groups.
- Ask questions to find out what interests other people.
- Ask questions and find out why people behave the way they do.
- Seek out opportunities where deep thinking is required.
- Seek solutions to difficult conceptual problems.
- Show trust in one’s own natural instincts, thereby taking risks.
- Look for challenges and consider them as opportunities to grow.


Creative Thinking
Creative Thinking is the ability to engage in the generation, evaluation and improvement of diverse ideas, which can result in original and effective solutions, advancement in knowledge and meaningful expressions of imagination. It involves making connections across topics, concepts, disciplines and methodologies.
Creative Thinking is a vital life skill which enables us to imagine, innovate and respond to unexpected or changing situations. It can improve other abilities like metacognition and problem-solving skills, as well as promote identity development, academic achievement, future career success and social engagement.
Creative Thinking In Action
The person will be able to :
- Follow new approaches and produce original ideas.
- See existing situations in new ways or improve on existing ideas.
- Act on intuition.
- Identify alternative explanations.
- Generate diverse and numerous ideas.
- Generate ideas that are relevant to the requirements of the problem/situation.
- Form unexpected combinations from available information to come up with solutions or new ideas.
- Engage in the task because they find it rewarding, enjoyable and challenging rather than for incentives offered.


Transformational Entrepreneurship
Transformational Entrepreneurship is the ability to create innovative solutions that enable change and maximize long-term economic and societal impact. It is about thinking beyond monetary goals, and the ability to take purposeful action towards creating systemic changes in the lives of individuals as well as organisations, leading to greater empowerment of people and society. It is the ability to approach problems systematically, address root causes, unlock human potential, enhance relationships and mutual learning.
Transformational Entrepreneurship is an important life skill for young people, to be drivers of humane, fair, inclusive and sustainable development.
Transformational Entrepreneurship In Action
The person will be able to:
- Take the initiative to visualise beyond the immediate or obvious goals.
- Proactively collaborate and nurture relationships and hold on to people
- Take risks and work with new people and approaches.
- Delay gratification and put others’ needs before their own
- Overcome obstacles and stay aligned to their goals despite difficulties.
- Seek a greater social purpose in their work.
- Advocate for causes that might not be business-oriented but contribute towards societal change.
- Solve complex social issues in fair, inclusive and sustainable ways.
- Create and offer opportunities for fair and equitable growth.


Resourcefulness
Resourcefulness is the ability to adapt to new or different situations, think creatively, find solutions and make the best use of the available resources. This ability helps us consider all possible ways for attaining what we desire and also make good use of the opportunities available to us. It includes working collaboratively in teams or with group members and optimizing their skills and resources towards attainment of goals.
Research has shown that students who are resourceful tend to perform well even under stress and adversity. Resourcefulness can be considered as one of the important skills to being active, thoughtful and participating members and leaders in society.
Resourcefulness In Action
The person will be able to:
- Come up with multiple approaches to working towards a goal.
- Brainstorm alternative solutions to various problems.
- Show the readiness to experiment and try out new methods.
- Show curiosity and engage with their environment and the people around them.
- Build an active network of friends and acquaintances.
- Build resources for personal as well as social purposes.
- Demonstrate perseverance by trying out all possible means to attain their goals.
- Seek help, information and perspectives of individuals or groups who can contribute towards their goal or purpose.
- Demonstrate awareness of their own skills, talents and strengths.

